Version control and track changes
Git, GitHub, Gitlab
An introduction to version control, easy to share/reproduce code, and more!
You can find it as a scrollable RevealJS presentation here.
By: L. Darmet and JJ. Torre



Version control can be a solution !
Use cases
- Keep track of file changes (also with Matlab..!) 🖥️
- Synchronize changes among team members 🤝
- Share the code along your publication: open science and open data 📡
- Yes you are ashamed to share your code but it would put a strain on you for better code (cleaner, clearer, etc) 🥲
- Sharing only data is sometimes harsh if you don’t provide an example on how to use them 🙏
- Maintain a code library 📚 to share existing code with new interns, PhD, collaborators,…
- Avoid developing again and again the same tools for experimental protocol, pre-processing, data visualization…
- Standard pipelines
- We have created a COPHY organization on GitHub to centralize code

- Manage and maintain the \(\LaTeX\) code of your thesis 🤓
- Overleaf supports direct sync with GitHub to import existing repos or create one based on current project. > This direct sync also allows to backup your Overleaf projects
Git + GitHub is the most common version control system
What are the differences between the two ?


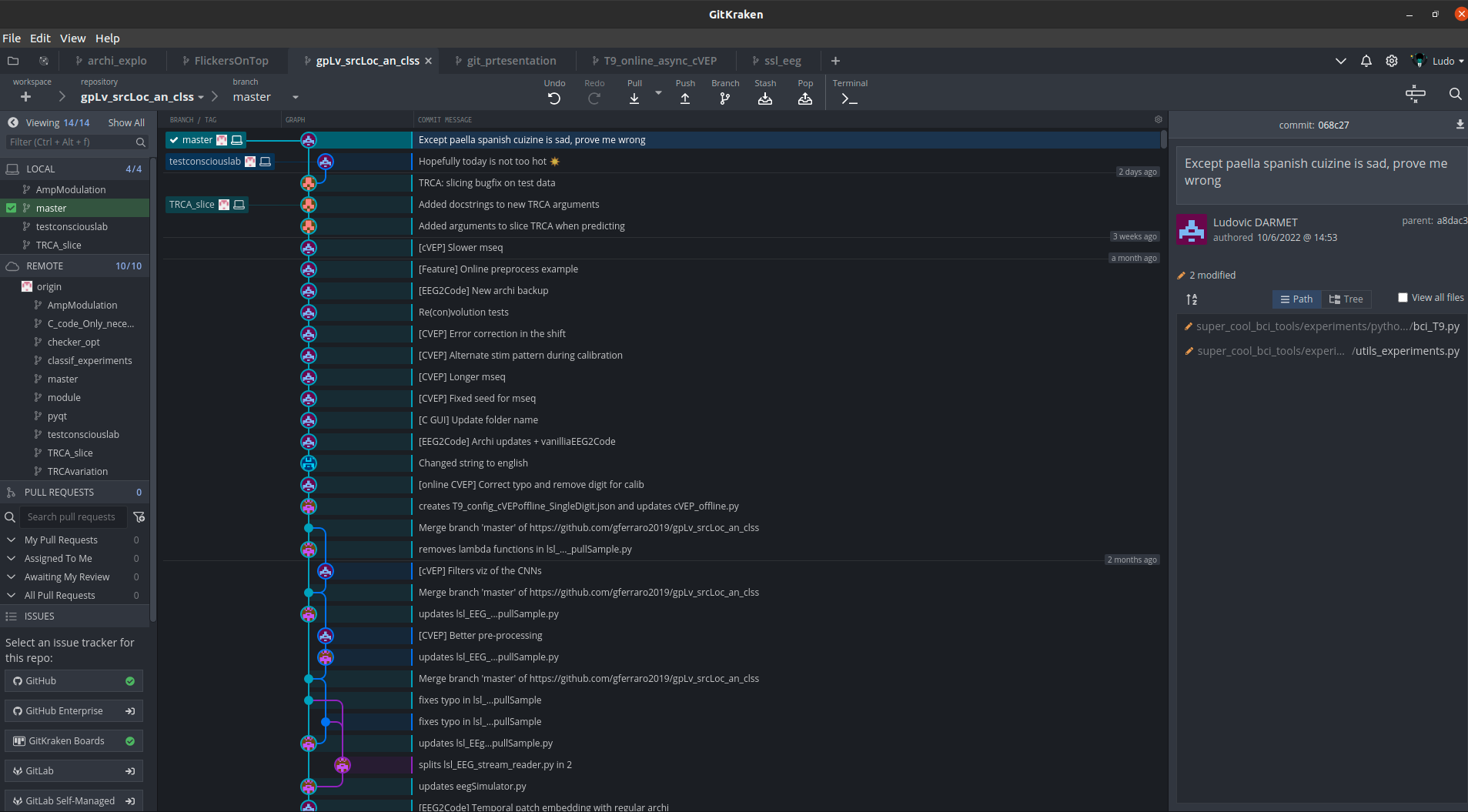
- Git is an open-source distributed version control tool
- It follows the evolution of a set of files in your computer, called a repository or repo
- Created by Linus Torvalds (creator of Linux and Android) in 2005 and maintaned by the Linux Foundation

- Github is an online hosting service for git repos
- Startup created in 2008, acquired by Microsoft in 2018
- The repos can be either private or public
- Additionnal features:
- Features requests, issues and pull request: ask for new functionnality and merge new functionnality to the exisiting code after review by the owner
- A wiki for each project
- Continuous integration tools (run automatic tests to check if additions in the code don’t alter the expected outputs)
- Host your personnal website
- Cute cat/octopus mascot
- Follow people and explore their code database
Personnal static website

- There exists other online hosting services such as Bitbucket (also private company) or Gitlab (open-source).
- We have a self-hosted Gitlab in CRNL..! 💫


Get GitHub for free
GitHub is free but you may encounter limitations if you do not suscribe to GitHub Pro (4$ per month 💸)
Because of your academic or student status you can get Github Pro for free.
Apply here: https://education.github.com/benefits

Or use the Gitlab of CRNL 🤯
- Open a ticket to ask access to the GitLab
- Sign in and connect in: http://10.69.168.17/users/sign_in

Terminology
- Create a repository or repo and clone it
- Commit your changes (locally) and then push (remote) \(\rightarrow\) keep track of changes/addition
- Pull to get latest changes from other people
- Going back to a previous commit
- Solve merge conflicts
- Use branch to develop features in parallel
Code example to start using Gitub 👩💻
Install Git on your machine
- On Linux from a terminal:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install git-all- On Windows:
- Download it from https://git-scm.com/download/win
- Run the installer
Create a local repo from scratch
Enter commands in GitBash for Windows and on terminal for Linux
mkdir mynewrepo && cd mynewrepo
git init
ECHO >> README.md
git add README.md
git commit -m "Add README"Connect your machine with GitHub
First you need to create an account on https://github.com
Then we will need SSH key to have a secure and authentified connection
- In terminal or GitBash, generate SSH keys:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "your_email@example.com"Use same email as registred on GitHub. Then press Enter two times (no need to set a password).
- Then open the generated (public) key to share it with GitHub:
notepad ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pubOn GitHub website go to: Settings > SSH and GPG Keys. Click on New SSH key and enter a title.
In the field Key paste all the contents of the file
id_rsa.pubthat you have just opened, beginning atssh-ras ...up to your email (including it). You can copy with a terminal utility (such asxclip) if copying by hand does not workClick Add SSH key
Connect your local repo to GitHub
As you have setup a secured SSH key, no need for password
Go back to you terminal where you have initialized your local repo:
git remote add origin git@github.com:username/new_repo
git push -u origin masterOr use a GUI for simpler interactions 🤓
- GitHub Desktop: from Github directly
- Gitkraken: the most comprehensive (requires GitHub Pro)

They also handle the SSH keys for you